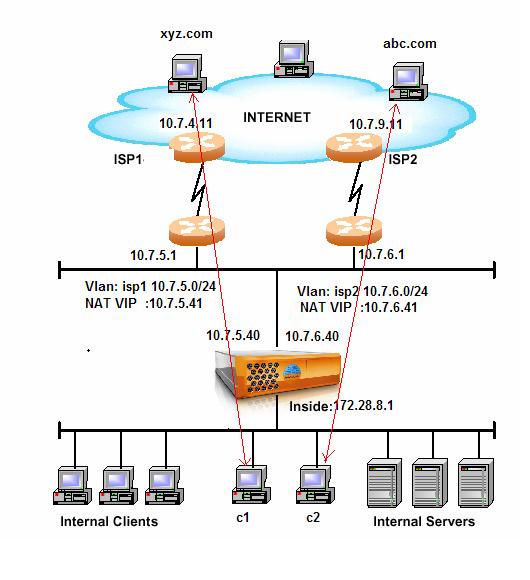
Outbound LLB
Outbound LLB integrates with
Internal clients push traffic to the inside NIC and LLB routes the traffic out accordingly base on the preset method(rr, wrr, dd, or sr).
Example:
C1 -> xyz.com LLB routes traffic to the isp1 link using NAT VIP 10.7.5.41.
C2 -> abc.com LLB routes traffic to the isp2 link using NAT VIP 10.7.6.41.
LLB is implemented at L3 (the IP layer), connection persistence is based on src:dst IP pair. Default persistence timeout is 60 second. Timeout value can be changed using "nat port" command.
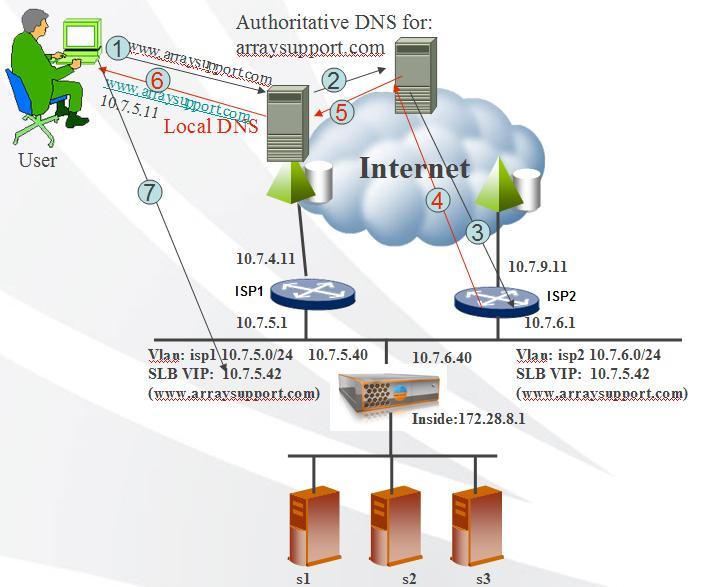
Inbound LLB
Inbound LLB integrates with RTS(Return-to-Sender) and DNS to direct external traffic through 2 or more external links.
One IP address from each ISP link listens on UDP port 53 for DNS queries.
When TMX sends return traffic back to the client, RTS helps to direct the traffic back to the same link as it came in.
Example:
1. User points his/her browser to www.arraysupport.com.
2. The user's computer sends a DNS query to it's local DNS and eventually the query gets to the authoritative DNS for arraysupport.com.
3. The authoritative DNS has preconfigured with 2 NS records (one points to the IP on ISP1 link and the other on ISP2 link) for resolving hostname www, so the query is forwarded to the currently active nameserver. In this case, the ISP2 link
4. TMX sends a response with the IP address from ISP1 back to the user through steps 5 and 6.
5. Refer to step 4.
6. Refer to step 4.
7. The user’s browser sends the request to the SLB vip on ISP1 link.