It is essential to take APV configuration backup before doing any changes on configurations or upgradation of OS version in the device. As it keeps all the configurations safe and can be restored in case of any configuration mismatch after the activity. Also in case of any hardware failure/replacement we can restore the configuration in new device and put it into production network.
Different Types of Backup procedure available.
Backup of configuration are two types:
-
All backup (Full backup)- In this all the configurations of the device including SSL certificates will be saved.
2. Running backup- In this the current running configuration is saved (doesn’t include SSL certificates).
BACKUP
Pre-requisites if backup via TFTP or SCP server
-
Install TFTP/SCP server in the laptop.
2. TFTP and SCP ports should be allowed on network firewall and other security devices.
Collecting Backup of APV using WebUI.
System > Config management > Backup
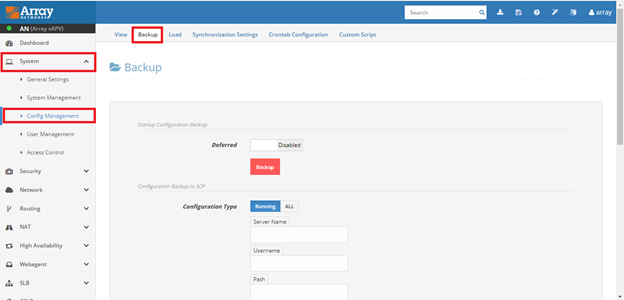
-
Collecting backup of running configuration / all configuration
1.1)Local Storage (APV device)
To save the running configuration to a backup file on the local storage(APV device) Enter file name and click on Backup.
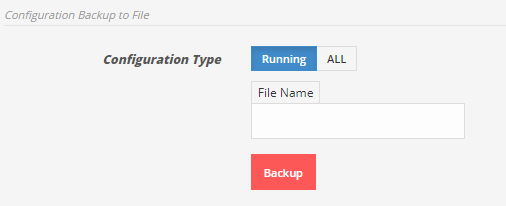
To save all backup configurations click on ALLfirst then enter file name, password and click Backup.
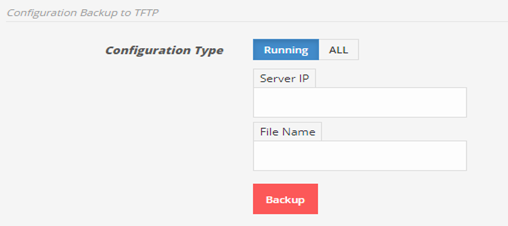
1.2)TFTP server
To save running configuration to TFTP server. Enter TFTP server IP, file name and click on Backup.
To save all backup configurations click on ALLfirst then enter TFTP server IP, file name, password and click Backup.
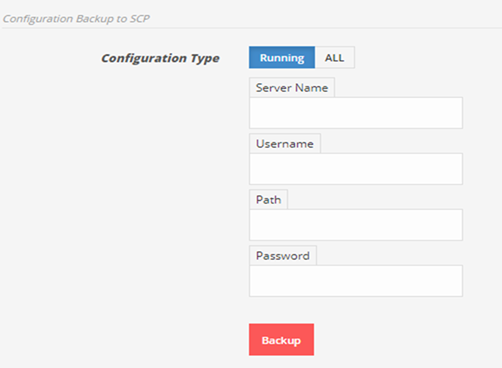
1.3) SCP server
To save running configuration to SCP server.
Enter SCP server IP, username, file name, password and click on Backup.
To save all backup configurations click on ALLfirst then enter SCP server IP, username, password, file name, password for file and click Backup.
1.4) Downloading both running and all configurations from APV to LAPTOP.
-
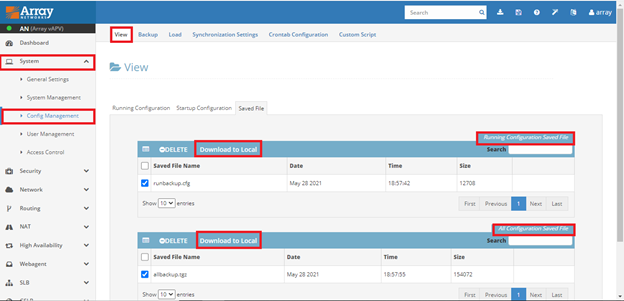
System à Config management à View
2. Select the desired file one at a time running or backup.
3. Click on download to local.
4. The file will be downloaded to your laptop.
Collecting Backup of APV using CLI
-
Collecting backup of running configuration
1.1 Local storage
To save current configuration execute “write memory”, then configuration goes to startup configuration.
To save the running configuration to a backup file on the local storage(in APV device).
write file <file name>
1.2 TFTP server
To save running configuration to TFTP server.
write net tftp <tftp_ip> <file_name>
ip_tftp: The IP address of the TFTP server.
file_name: The name of the remote file in which the configuration data
is saved. It is optional, and defaults to “ca.cfg”
1.3 SCP server
To save running configuration to SCP serverwith password authentication enabled.
write net scp {remote_server_ip|name} <user_name> <config_file_name>
server ip: IP of scp server (in quotation marks) or name of the server.
user_name: User’s name for remote SCP server being accessed.
config_file_name: The name of the remote file in which the configuration data
Note: A password authentication for the user will be prompted for the remote server which will appear after executing this above command.
2.Collecting backup of all configurations
2.1 Local storage
To save the all configuration to a backup file on the local storage(in APV device itself) to a specific TGZ file.
write all file <file name> <password>
file name: User assigned name for TGZ file. It should not contain extension name “.tgz”.
password: The password for accessing the TGZ configuration backup file. Its value supports letters, numbers and the following special characters: “~”, “@”,“#”, “%”, “^”, “&”, “*”, “(”, “)”, “-”, “_”, “+”, “=”, “”, “{”, “}”, “[”, “]”, “'”, “:”, “;”, “”, “|”, “”, “,”, “.”, “?” and “/”. When the parameter value contains special characters, it must be enclosed by double quotes.
2.2 TFTP server
To save all configuration to a remote host via the TFTPprotocol.
write all tftp <tftp_ip> <remote_file_name> <password>
ip_tftp: The IP address of the TFTP server.
file_name: The name of the remote file in which the configuration data with .tgz extension.
password: The password for accessing backup file saved on the remote host (in double quotes)
2.3 SCP server
To save all configuration to a remote host via the SCPprotocol
write all scp <server_name> <user_name> <remote_file_path> <password>
server ip: IP of scp server (in quotation marks) or name of the server.
user_name: User’s name for remote SCP server being accessed.
remote_file_name: The path to save the configuration file on the remote host.
(Eg:/abc.tgz)
password: The password used for accessing backup configuration file saved on the remote host (in double quotes)
RESTORATION
Restoring Backup of APV using WebUI
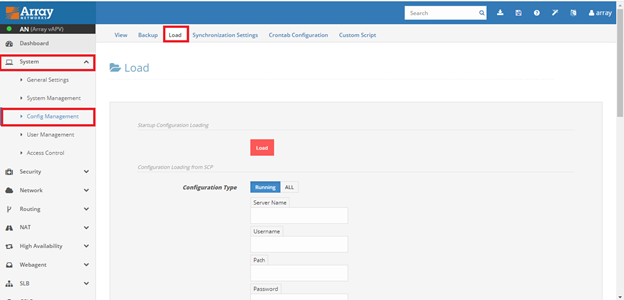
System > Config management > Load
-
Restoring backup of running configuration / all configuration
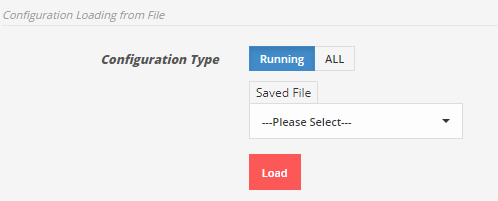
1.1 From Local storage
To restore the running configuration from local storage (APV device), select file from drop down list.
To restore all backup configuration, click on ALLfirst then select file from drop down list, enter associated password for that file and click Load.
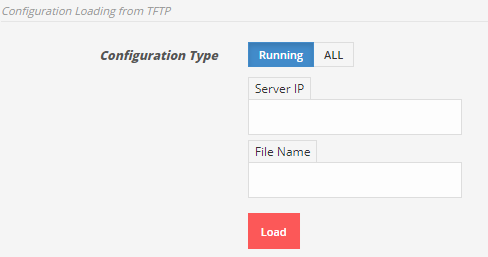
1.2 From TFTP server
To restore running configuration from TFTP server. Enter TFTP server IP, file name and click on Load.
To restore all backup configuration, click on ALLfirst then enter TFTP server IP, file name, password of associated file and click Load.
1.3 From SCP server
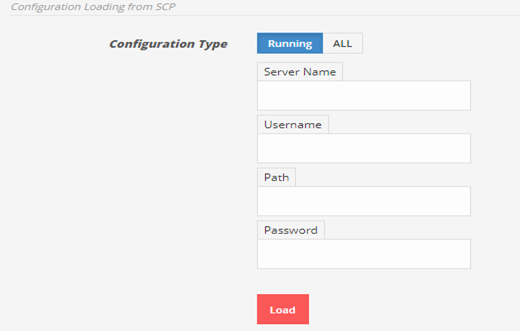
To restore running configuration from SCP server. Enter SCP server IP, username, file name, user password and click on Load.
To restore all backup configuration, click on ALLfirst then enter SCP server IP, username, user password, file name, password of the associated file and click Load.
1.4 From LAPTOP
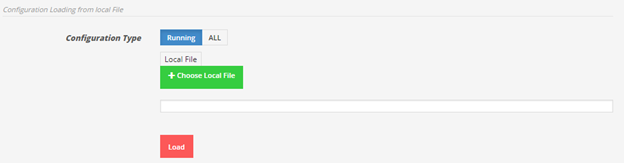
To restore running configuration from laptop. Choose the desired file and click on Load.
To restore all backup configuration, click on ALL then choose the file, enter password of the associated file and click Load.
Restoring Backup of APV using CLI
-
Restoring the running configuration file
1.1 From local storage
To restore the configuration from the last “write memory” operation, execute “config memory”.
To restore configuration backup file from local device(APV device) by giving saved file’s name.
config file <file_name>
1.2 From TFTP server
To restore file from TFTPserver.
config net tftp <tftp_server_ip> <config_file_name>
The ip address should be in double quotes or name of the TFTP server and file name should be supplied.
1.3 From TCP server
To restore file from SCPserver by executing below command.
config net scp {remote_server_ip|name} <user_name> <config_file_path>
The IP address (in quotation marks) or the name of the SCP server, the user’s name for the remote machine being accessed (a password prompt for the remote machine will appear) and the remote file path must be supplied.
2. Restoring all configurations file
2.1) From local device
To restore all configuration (TGZ) backup file from local APV deviceby giving saved file name.
config all file <file_name > <password>
file_name: File name without .tgz extension.
password: Password in double quotes.
2.2 From TFTP server
To restore all configuration file from TFTPserver
config all tftp <tftp_ip> <remote_file_name> <password>
tftp_ip: The IP address of the remote host.
remote_file_name: The name of the configuration file on the remote host.
password: The password used for accessing backup.conf in the
configuration file saved on the remote host. If a wrong
password is input, backup.conf in the configuration file
cannot be decrypted and restored.
2.3 From SCP server
To restore all configuration file from SCPserver
config all scp <server_name> <user_name> <remote_file_path> <password>
server_name: The host name or IP address of the remote host.
user_name: The username to access the remote host.
remote_file_path: The path of saving the configuration file on the remote host.
password: The password for accessing backup.conf in the configuration file saved on the remote host. If a wrong password is input, backup.conf in the configuration file cannot be decrypted and restored.









