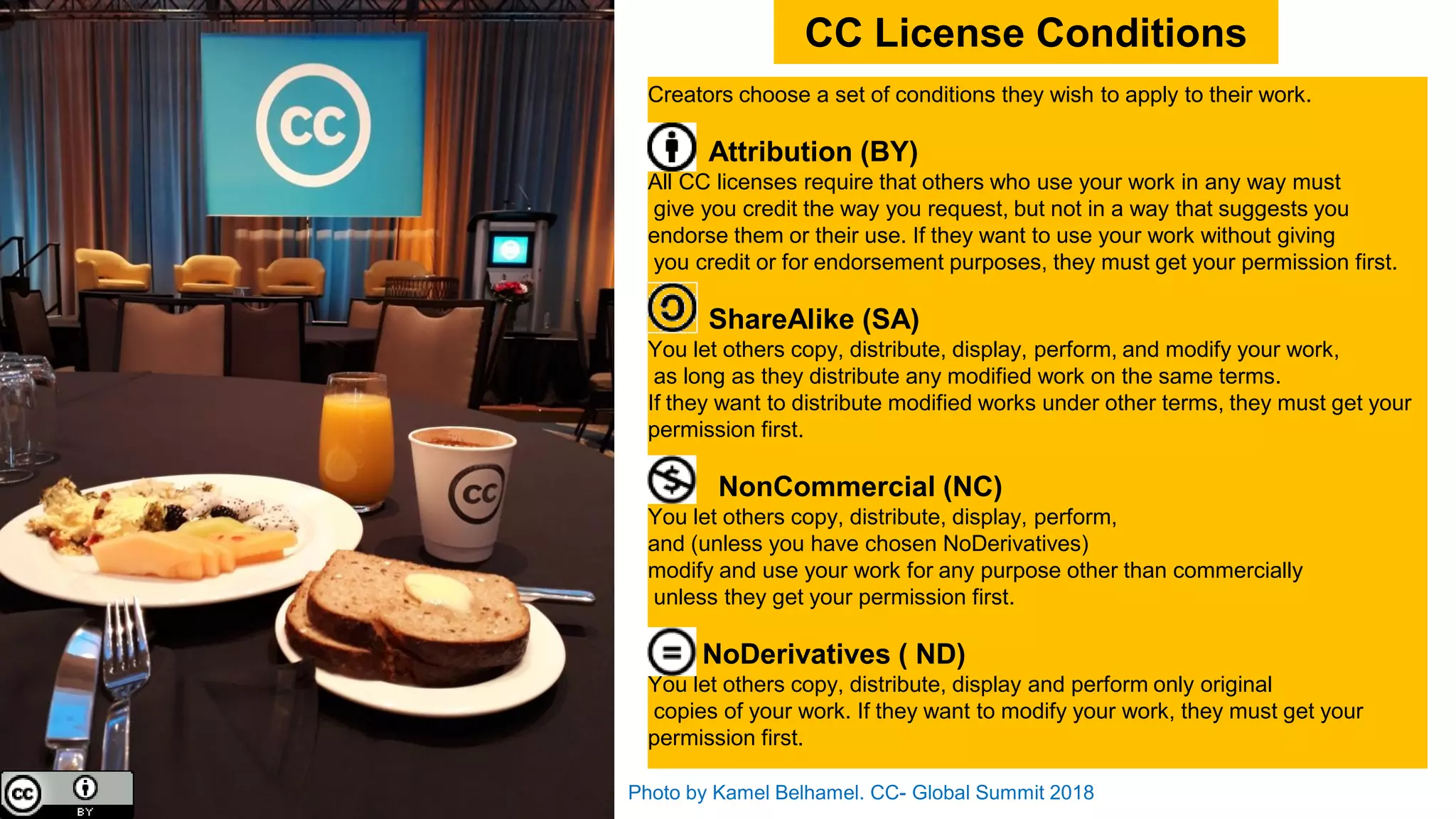
The document discusses the Creative Commons (CC) organization, which was established to facilitate sharing and reuse of creative works while addressing the limitations imposed by full copyright. It outlines the background of copyright concerns, including the Sonny Bono Copyright Term Extension Act and the Eldred v. Ashcroft case, which questioned copyright duration. Additionally, it details the CC licenses that allow creators to define how their works can be used, promoting legal sharing and adaptation within the digital landscape.