Making the most of New CSS Layout
- 1. Making the most of New CSS Layout Rachel Andrew, SmartWeb, Bucharest 2016
- 2. Rachel Andrew rachelandrew.co.uk @rachelandrew CSS Working Group Invited Expert Google Developer Expert for Web Technologies Co-founder Perch CMS: https://grabaperch.com Contact: me@rachelandrew.co.uk
- 3. Modern CSS Layout? • Floats • Inline-block • display: table • Absolute & Relative positioning • Frameworks … lots of frameworks
- 4. Snippet from Bootstrap Grid mark-up. <div class="row"> <div class="col-md-8"> .col-md-8 <div class="row"> <div class="col-md-6"> .col-md-6 </div> <div class="col-md-6"> .col-md-6 </div> </div> </div> <div class="col-md-4"> .col-md-4 </div> </div>
- 5. Our great hopes for layout • Flexbox https://drafts.csswg.org/css-flexbox/ • CSS Grid Layout https://drafts.csswg.org/css-grid/ • Box Alignment https://drafts.csswg.org/css-align/
- 9. The new CSS for Layout
- 10. Items in our layouts understand themselves as part of a complete layout.
- 13. Flexbox Full height columns with flexbox, taking advantage of default alignment values. .wrapper { display: flex; } .sidebar { flex: 1 1 30%; } .content { flex: 1 1 70%; }
- 14. Grid Layout Full height columns in CSS Grid Layout. .wrapper { display: grid; grid-template-columns: 30% 70%; } .sidebar { grid-column: 1; } .content { grid-column: 2; }
- 15. Separation of source and display
- 16. Flexbox The flex-direction property can take a value of row to display things as a row or column to display them as a column. nav ul{ display: flex; justify-content: space-between; flex-direction: row; }
- 17. Flexbox The visual order can be switched using row-reverse or column- reverse. nav ul{ display: flex; justify-content: space-between; flex-direction: row-reverse; }
- 18. Flexbox Adding display: flex to our container element causes the items to display flexibly in a row. .wrapper { display: flex; }
- 19. Flexbox The order property means we can change the order of flex items using CSS. This does not change their source order. li:nth-child(1) { order: 3; } li:nth-child(2) { order: 1; } li:nth-child(3) { order: 4; } li:nth-child(4) { order: 2; }
- 20. Grid Layout I have created a grid on my wrapper element. The grid has 3 equal width columns. Rows will be created as required as we position items into them. .wrapper { display: grid; grid-template-columns: 1fr 1fr 1fr; }
- 21. Grid Layout I am positioning my elements using CSS Grid Layout line-based positioning. Setting a column and a row line using the grid- column and grid- row properties. li:nth-child(1) { grid-column: 3 ; grid-row: 2 ; } li:nth-child(2) { grid-column: 1 ; grid-row: 2 ; } li:nth-child(3) { grid-column: 1 ; grid-row: 1 ; } li:nth-child(4) { grid-column: 2 ; grid-row: 1 ; }
- 23. CSS Grid automatic placement http://www.w3.org/TR/2015/WD-css-grid-1-20150917/#grid- auto-flow-property https://rachelandrew.co.uk/archives/2015/04/14/grid-layout- automatic-placement-and-packing-modes/
- 25. Grid Layout When using automatic placement we can create rules for items in our document - for example displaying portrait and landscape images differently. .wrapper { display: grid; grid-template-columns: 1fr 1fr 1fr 1fr; grid-template-rows: auto; } .landscape { grid-column-end: span 2; }
- 26. grid-auto- flow The default value of grid- auto-flow is sparse. Grid will move forward planning items skipping cells if items do not fit .
- 27. Grid Layout With a dense packing mode grid will move items out of source order to backfill spaces. .wrapper { display: grid; grid-template-columns: 1fr 1fr 1fr 1fr; grid-template-rows: auto; grid-auto-flow: dense; } .landscape { grid-column-end: span 2; }
- 28. grid-auto- flow With grid-auto-flow dense items are displayed out of source order. Grid backfills any suitable gaps.
- 29. With great power comes responsibility.
- 30. Power and responsibility • Good = creating the most accessible source order and using Grid or Flexbox to get the optimal display for each device. • Bad = using Grid or Flexbox as an excuse to forget about the source. • Terrible - stripping out semantic elements to make everything a grid or flex item.
- 31. https://drafts.csswg.org/css-flexbox/#order-accessibility Authors must use order only for visual, not logical, reordering of content. Style sheets that use order to perform logical reordering are non- conforming.
- 32. Léonie Watson | On CSS accessibility and drinking tea | CSS Day 2016 https://vimeo.com/180566024
- 34. CSS Box Alignment Module Level 3 “This module contains the features of CSS relating to the alignment of boxes within their containers in the various CSS box layout models: block layout, table layout, flex layout, and grid layout.” - https://drafts.csswg.org/css-align/
- 35. It’s 2016. We can now centre things.
- 36. Box Alignment Properties - justify-content - align-content - justify-self - align-self - justify-items - align-items
- 37. Flexbox The justify- content property is set to space- between. The items at each end are placed against the container and the remaining space distributed evenly. nav ul{ display: flex; justify-content: space-between; flex-direction: row; }
- 38. Flexbox The justify- content property is set to space- around. The items are evenly distributed in the container with a half size space at each end. nav ul{ display: flex; justify-content: space-around; flex-direction: row; }
- 39. Grid If there is space in the grid container after all column and row tracks have been added. Use space-around and space- between to space the tracks. .wrapper { width: 500px; height: 400px; display: grid; grid-gap: 10px; grid-template-columns: repeat(4, 80px); grid-template-rows: repeat(3,100px); align-content: space-around; justify-content: space-between; }
- 40. Flexbox The value of align- items is stretch by default. If I add extra text in one navigation point the others all take the same height. nav ul{ display: flex; justify-content: space-around; flex-direction: row; align-items: stretch; }
- 41. Flexbox If I set the value of align-items to center then we get vertical centring. nav ul{ display: flex; justify-content: space-around; flex-direction: row; align-items: center; }
- 42. My grid has an absolute width and height. This is larger than required for the tracks. .wrapper { width: 500px; height: 400px; display: grid; grid-gap: 10px; grid-template-columns: repeat(4, 80px); grid-template-rows: repeat(3,100px); }
- 43. The align-content property controls the block axis. This axis aligns the grid rows. .wrapper { width: 500px; height: 400px; display: grid; grid-gap: 10px; grid-template-columns: repeat(4, 80px); grid-template-rows: repeat(3,100px); align-content: end; }
- 44. The justify- content property controls the inline axis. This axis aligns the grid columns. .wrapper { width: 500px; height: 400px; display: grid; grid-gap: 10px; grid-template-columns: repeat(4, 80px); grid-template-rows: repeat(3,100px); align-content: end; justify-content: center; }
- 45. I can create this same layout with flexbox or Grid. With flexbox the items are laid out in a row. .wrapper { display: flex; } .wrapper li { flex: 1 0 25%; }
- 46. The first item is at the default stretch and as the tallest item is dictating the height of the flex container. The second is entered in the container. The third aligned to the start. The fourth aligned to the end. .wrapper li:nth-child(2) { align-self: center; } .wrapper li:nth-child(3) { align-self: flex-start; } .wrapper li:nth-child(4) { align-self: flex-end; }
- 47. For Grid I use a single row, 4 column Grid. .wrapper { display: grid; grid-template-columns: 1fr 1fr 1fr 1fr; }
- 48. Grid alignment properties for the three landscape images. .wrapper li:nth-child(2) { align-self: center; } .wrapper li:nth-child(3) { align-self: start; } .wrapper li:nth-child(4) { align-self: end; }
- 50. 100vh body { align-content: center; justify-content: center; }
- 51. Aligning the grid. body { height: 100vh; display: grid; grid-template-columns: 80%; align-content: center; justify-content: center; }
- 53. 1fr 1fr 1fr 1fr 1fr 2fr 2fr .login > div .login > div .login > div.actions
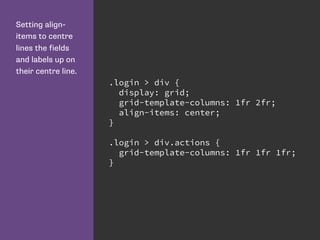
- 54. Setting align- items to centre lines the fields and labels up on their centre line. .login > div { display: grid; grid-template-columns: 1fr 2fr; align-items: center; } .login > div.actions { grid-template-columns: 1fr 1fr 1fr; }
- 56. Ethan Marcotte, Fluid Grids “… every aspect of the grid—and the elements laid upon it—can be expressed as a proportion relative to its container.”
- 57. target ÷ context = result h1 { margin-left: 14.575%; /* 144px / 988px = 0.14575 */ width: 70.85%; /* 700px / 988px = 0.7085 */ }
- 58. Flexbox The most simple flexbox example demonstrates the inherent flexibility. The items will be displayed as a row, with equal space between each item. nav ul{ display: flex; justify-content: space-between; }
- 59. The flex property • flex-grow - add space • flex-shrink - remove space • flex-basis - the initial size before any growing or shrinking
- 60. Flexbox flex: 1 1 300px; flex-grow: 1 flex-shrink: 1; flex-basis: 300px; The initial width of our li is 300 pixels, however it can grow larger and shrink smaller than 300 pixels. .wrapper { display: flex; } .wrapper li { flex: 1 1 300px; min-width: 1px; }
- 62. Flexbox flex: 1 1 300px; flex-grow: 1 flex-shrink: 1; flex-basis: 300px; If we allow the flex items to wrap we can see how flex-basis works by dragging the window smaller. .wrapper { display: flex; flex-flow: row wrap; justify-content: space-around; } .wrapper li { flex: 1 1 300px; min-width: 1px; }
- 64. Flexbox flex: 1 1 300px; flex-grow: 1; flex-shrink: 1; flex-basis: 300px; The 3rd item has flex: 0 1 300px; so cannot grow. .wrapper { display: flex; } .wrapper li { flex: 1 1 300px; min-width: 1px; } .wrapper li:nth-child(3) { flex: 0 1 300px; }
- 66. Flexbox If we set the 3rd item to flex-grow: 2 This item will be assigned twice of much of the available free space after we have reached the 300 pixel initial width. .wrapper { display: flex; } .wrapper li { flex: 1 1 300px; min-width: 1px; } .wrapper li:nth-child(3) { flex: 2 1 300px; }
- 69. The CSS Grid Layout fr unit
- 70. Grid Layout I am creating three grid column tracks, all 1fr in width. This gives me three equally sized column tracks. .wrapper { display: grid; grid-template-columns: 1fr 1fr 1fr; }
- 71. Grid Layout If I create the first column as 600 pixels and then have two 1fr columns the 600 pixel track is removed from the available space and the remainder is distributed equally between the two columns. .wrapper { display: grid; grid-template-columns: 600px 1fr 1fr; }
- 72. Grid Layout With a 600 pixel column, a 1fr and a 3fr column. The 600 pixels is removed from the available space then the remaining space is divided by 4. The 1fr column gets 25% and the 3fr column 75%. .wrapper { display: grid; grid-template-columns: 600px 1fr 3fr; }
- 74. Flexbox for 1 dimensional layout. CSS Grid is for 2 dimensional layout.
- 76. The value of the grid-template- columns property says: repeat this track listing, auto-filing as many columns with a minimum width of 300 pixels and a maximum of 1fr. .wrapper { display: grid; grid-template-columns: repeat(auto-fill, minmax(300px, 1fr)); }
- 82. Using the minmax() function with grid-auto-rows. .home-hero { display: grid; grid-gap: 1px; grid-auto-rows: minmax(150px, auto); }
- 83. An item on the grid can become a grid or flex container itself. In this case I am using flexbox and auto margins to push my content to the bottom of the box. .special { display: flex; flex-direction: column; } .special h3{ margin-top: auto; }
- 86. Say hello to Feature Queries.
- 87. I have set three classes to display: none; .has-flex, .has-grid, .has-grid-shapes { display: none; }
- 88. My @supports rule tests for support of the display property with a value of flex. If it is supported we show the div. @supports (display: flex) { .has-flex { display: block; } }
- 89. My @supports rule tests for support of the display property with a value of grid. If it is supported we show the div. @supports (display: grid) { .has-grid { display: block; } }
- 90. My @supports rule tests for support of the display property with a value of grid AND shape- outside:circle. If it is supported we show the div. @supports (display: grid) and (shape-outside:circle()) { .has-grid-shapes { display: block; } }
- 93. Defaults for all browsers will be loaded by even really old browsers. body { padding-top: 20%; } h1, .login, .account, .contact{ width:80%; margin: 0 auto; }
- 95. Within a Feature Query we add some information for flexbox supporting browsers. @supports (display: flex) { body { padding:0; height: 100vh; display: flex; align-items: center; justify-content: center; flex-direction: column; } h1, .login, .account, .contact { margin: 0; width: 80%; } }
- 97. The Feature Query for Grid supporting browsers. @supports (display: grid) { body { display: grid; grid-template-columns: 80%; align-content: center; align-items: stretch; } @media (min-width: 650px) { body { grid-template-columns: repeat(2, minmax(150px, 30%)); } h1, .login { grid-column-end: span 2; width: auto; } .login > div { display: grid; grid-template-columns: 1fr 2fr; align-items: center; } .login > div.actions { grid-template-columns: 1fr 1fr 1fr; } .account { border-right: 1px dotted rgb(191, 216, 227); padding: 0 10px 0 0; align-self: end; width: auto; } .contact { padding: 0 0 0 10px; width: auto; } } }
- 98. Your users ‘grow into’ enhancements as their browsers auto-update.
- 101. Why are we looking at something I can’t use yet?
- 103. Get involved with developing specs! • While a spec is being developed your feedback is wanted and can be included in the spec. • Wait until browsers ship and you lose that chance. • It just got easier. CSS Spec issues are now on GitHub. http://logs.csswg.org/irc.w3.org/css/2016-05-10/#e684439
- 104. Do a good deed for your future self.
- 105. Thank you Slides & Resources: https://cssgrid.me/SmartWeb16-slides http://csslayout.news - sign up for my weekly CSS Layout email — @rachelandrew | me@rachelandrew.co.uk — https://rachelandrew.co.uk | https://grabaperch.com